Today, the word “Benchmarking” has gained popularity and plays a crucial role in improving the performance of businesses. Understanding “What is Benchmarking” and its importance will help businesses seize opportunities to overcome competition and develop sustainably. Let’s learn about this concept and its importance in effective business management.
What is Benchmarking?

Benchmarking is the process of comparing and learning from excellent companies or organizations to improve your own performance.
Specifically, Bench-marking will identify internal improvement opportunities by studying businesses that are outperforming. Then analyze what makes that performance stand out, compare it with your business, and start making changes to deliver significant improvements.
Example: Your business provides a service that has an 80% customer satisfaction rate. This figure may seem good and even higher than the industry average. However, if some other companies (not necessarily direct competitors) achieve a 93% satisfaction rate, it raises a concern. In this situation, the 80% satisfaction rate of your business needs to be reevaluated. To gain a better understanding of the situation and improve the performance of your business, managers use “bench-marking.”
The Role Of Benchmarking

For businesses, Benchmarking helps them determine the relative distance between the quality of their products/services and those of their competitors, thereby making appropriate adjustments to increase the quality of those products/services.
For customers and consumers, Bench-marking is a relatively reliable method to compare products/services, thereby helping customers and consumers choose the right product/service for their needs.
Benefits of Benchmarking

Benchmarking is an important tool that helps businesses achieve many important benefits. Here are some of the key benefits of Benchmarking:
- Discover strengths and weaknesses: Bench marking allows a business to compare its performance and processes with those of competitors or excellent businesses. As a result, they can identify strengths that need further development and weaknesses that need to be overcome.
- Position in the market: Benchmarking provides an overview of the position of the business in the industry and market. It gives you a clear understanding of how your business stands compared to your competitors and industry leaders.
- Promote innovation and creativity: Bench marking is not only about copying what has been successful but also encouraging innovation and creativity. By embracing new trends and technological advancements, businesses can develop new solutions and create a competitive advantage.
- Encourage healthy competition: Bench marking motivates competing businesses to become better. By learning and sharing information, businesses encourage each other to become better, promoting the sustainable development of the whole industry.
- Capture industry trends: By comparing with leading companies, businesses can capture the latest industry trends and standards. This helps them stay up to date with technological advancements and apply innovative solutions to improve business operations.
- Enhance efficiency and performance: Thanks to Bench-marking, businesses can adopt best practices and processes from other excellent businesses. This improves their overall efficiency and performance.
- Raise awareness and learn: Bench-marking provides an opportunity to learn from people who have been successful in similar businesses. Businesses can learn from the mistakes and successes of others to make better decisions in the future.
Limitations of Benchmarking

While benchmarking is a useful tool for finding improvement opportunities and learning from excellent organizations, it also comes with some limitations to consider:
- Challenging Data Collection: Gathering information from other businesses can be difficult and requires their cooperation. Each company has its own data management system, and the willingness to share information may vary, potentially reducing the accuracy and integrity of bench-marking data.
- Unfair Comparisons: Some businesses may not provide complete or accurate performance information, leading to unfair or inaccurate comparisons. Some may choose to share only positive data to create a better impression.
- Not Suitable for Every Situation: Bench marking is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Unique and complex processes within each business can make comparisons challenging and ineffective.
- Time and Cost-Intensive: Bench-marking demands significant resource investment, including time, money, and personnel. Gathering and analyzing data from different businesses, conducting surveys or site visits, and developing improvement plans can be costly.
- Risk of Inappropriate Copying: In some cases, companies may blindly copy models from competitors without considering their suitability for their own circumstances. This can lead to the application of inappropriate processes and negative consequences.
- Data may become outdated: Benchmarking relies on information and data from current businesses. However, in a constantly changing business environment, this information may become outdated and no longer relevant to the current situation. This can lead to erroneous decisions based on outdated data.
Types of Benchmarking
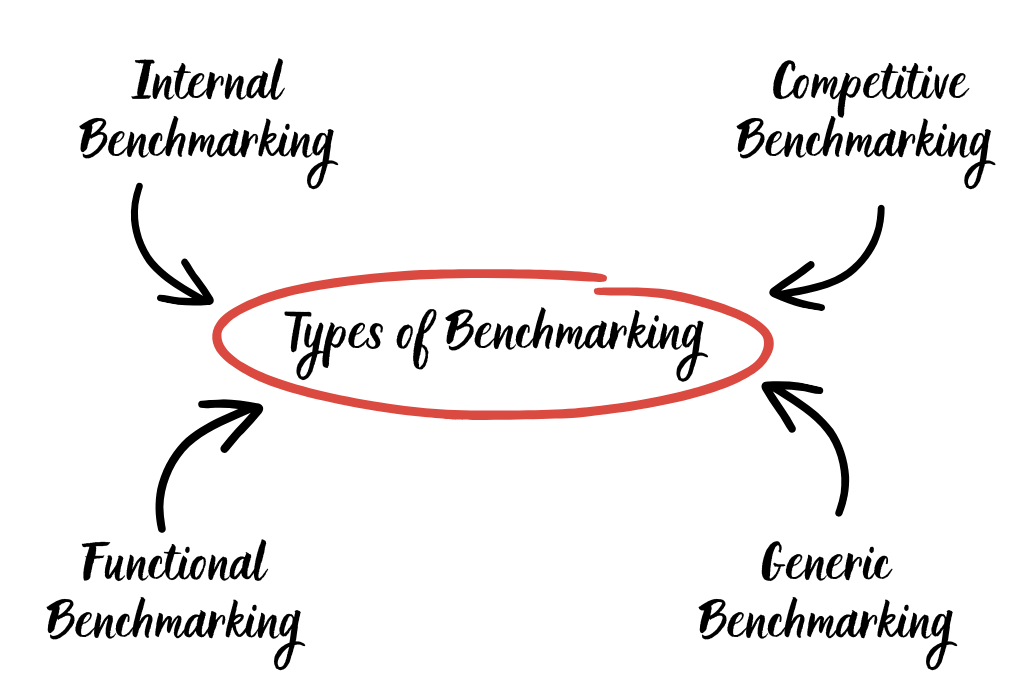
Each type of benchmarking has a different goal and scope. The flexible use of these types of benchmarks will help businesses get an overview of their position in the market and find ways to improve performance and competition in their industry. Benchmarking can be divided into the following categories:
1. Internal Benchmarking
- Compare performance and processes across departments or branches within the same business.
- Used to find improvement opportunities and share best practices across parts of the business.
For instance, you can compare the performance of one warehousing and shipping site to the performance of another warehousing and shipping site. The site with higher performance just needs to share its techniques and practices with the rest of the firm so that everyone benefits from improved performance.
2. Competitive Benchmarking
- Compare your business’s performance with that of direct competitors.
- Used to assess a business’s position in the market and find opportunities for improvement to compete more effectively.
For example, you can compare a competitor’s product’s customer satisfaction to yours. If your competition has superior customer ratings, you should investigate why and figure out how to improve the quality of your product.
3. Functional Benchmarking
- Compare specific functions or processes of your business with those of other companies operating in the same industry.
- Used to identify best practices and superior standards in a particular area to improve your own processes.
For example, If your company wants to improve its supply chain management, you can conduct functional benchmarking by comparing your supply chain processes with those of the leading companies in your industry. By analyzing their efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and responsiveness, you can learn from their successful approaches and implement your own supply chain management improvements.
4. Generic Benchmarking
- Compare your business’s processes and operations with those of companies from different industries.
- Used to discover best practices and innovative approaches that can be adapted to your own business for improvement.
For example, if your business wishes to improve customer service, you can conduct general benchmarking by researching the customer service practices of companies known for their exceptional customer experience, even if they’re not in the same industry as you. By examining their processes, you can gain useful insights and tactics that you can apply to your own customer service operations, increasing client happiness and loyalty.
6 Steps In The Benchmarking Process
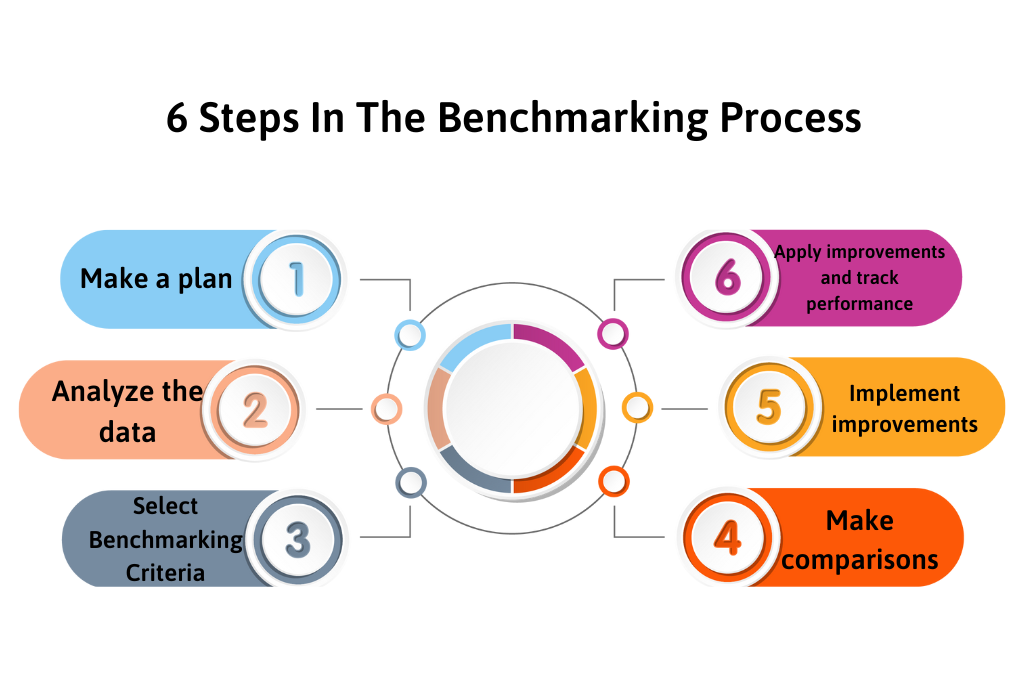
The benchmarking process not only helps businesses understand their position in the market but also helps them identify opportunities for improvement and drive sustainable growth. It includes the following steps:
Step 1: Make a plan
This stage is considered the most important when performing Benchmarking. The tasks to be done include: Presenting the problems the business wants to improve, information about competitors, and goals to be achieved. Once these tasks are completed, you can move on to the next step.
Step 2: Analyze the data
Data analysis is an important step in the benchmarking process, providing insight into the performance and operations of an organization or process relative to selected measurement standards. During the analysis phase, the following important tasks should be carried out:
- Gather the information needed to determine the extent to which improvement is needed.
- Compare the current process with appropriate reference models to find differences and innovations.
- Based on the results of the analysis, implement measures to improve and change the organization’s processes or operations.
Step 3: Select Benchmarking Criteria
Identify the criteria that you will use to measure your performance or process. This gives you a basis to compare and evaluate differences between businesses or processes. Ensure that measurement standards are aligned and compatible with the organization’s overall business strategy.
Choose metrics that really matter and can be measured accurately and reliably. Avoid choosing criteria that are too complicated or cannot be measured unambiguously.
Step 4: Make comparisons
Compare the collected data and information with selected measurement standards. Assess the degree of difference and similarity between the measured factors.
Based on the results of the comparison, analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the organization or process against the measurement standard.
Step 5: Implement improvements
Based on the analysis of the results, identify opportunities for improving the performance or processes of your organization. Learn from the best practices of competitors or other industries that can be applied to your organization.
Implement measures to improve and adjust the organization’s processes or activities to improve performance and achieve benchmarking objectives.
Step 6: Apply improvements and track performance
Based on the results of the analysis, implement measures to improve and change the organization’s processes or operations.
Monitor the effectiveness of implemented improvement measures to ensure that they achieve their goals and deliver value to the organization.
Conclusion
So, now you know “what is Benchmarking”, its benefits, and the steps to best practices benchmarking. Benchmarking is considered one of the management tools that has been effective in quality improvement management. By learning from the successes and failures of others, businesses can enhance their performance and competitiveness, leading to sustainable growth and breakthroughs in their businesses.
Follow ShineApps to get interesting knowledge. Thank you for reading!